/r/learnjavascript
This subreddit is for anyone who wants to learn JavaScript or help others do so.
Questions and posts about frontend development in general are welcome, as are all posts pertaining to JavaScript on the backend.
This subreddit is a place for people to learn JavaScript together. Everyone should feel comfortable asking any and all JavaScript questions they have here.
With a nod to practicality, questions and posts about HTML, CSS, and web developer tools are also encouraged.
Posting and Commenting Guidelines
- Be Welcoming. n00bs are welcome here. Negativity is not.
- Include Context. If you’re asking for help, include enough information for others to recreate your problem.
No Self-Promotion. The following are not allowed: Requests for subscribers, asking for "test users" for your new JS course, offering paid mentorships, and/or premium courses. Even if there is a coupon discount, no. If you're in doubt, message the mods first.
Good Titles - Write a descriptive title. Titles that begin with "hey guys" will be removed.
Related Subreddits
If you want to post something self-promotional, please message the mods first. Personal blog posts that are relevant to the subreddit's stated subject matter don't need prior approval (and are encouraged!).
/r/learnjavascript
271,364 Subscribers
I'm working on a library that should run on node or in browser. Trying to use Node Crypto or window.crypto depending on the environment. Is this a good way to do this?
As the title says, this is the code I've got, which seems to work:
if (typeof process !== 'undefined' && process.versions && process.versions.node) { ...use node...
else if (typeof globalThis !== 'undefined' && 'crypto' in globalThis && 'getRandomValues' in globalThis.crypto) { ...use window.crypto...Is there a more standard way to do this? Any gotchas I should be aware of?
01:10 UTC
There are a lot of ways to break up long tasks in JavaScript.
You might've used something like setTimeout() to break apart a long, expensive task before. Well... especially as of recently, there are quite a few different ways to do this, each with its own tradeoffs. I wrote about a few of them if you wanna check them out:
01:04 UTC
What is your aha! moment
Professional, or someone know how to code what is your AHA moments. Im curious how or when do you know that you understand how to program and know you can build something. I think im almost there because i only lack of problem solving
22:53 UTC
Following the TOR spec doesn't produce a valid onion address [for me]
Following this spec: https://spec.torproject.org/rend-spec/encoding-onion-addresses.html
And this video: https://youtu.be/kRQvE5x36t4?si=pfzhfeu74SDq-suU
Produces: https://pastebin.com/8YQr29UM
The base32 library is: npm install base32
What am I doing wrong?
19:09 UTC
Would it be possible to make "Kotlin" of JS to make web development better?
I've been learning Kotlin recently and it's such an amazing language that is fully compatible with Java or other JVM languages such as Scala or Groovy. It is a lean language with all the boilerplatey parts of Java cut out, and has great balance between OOP and FP.
I wonder if same thing can happen about JS. Make a language of static type, good OOP & type system, support for FP, compatible with Node & Web API so they can be imported directly, whilest not having all the stinky parts of JS. Produces compiled code that runs on V8 and JavaScriptCore.
I mean JS also has its 'VM'. Although Java is compiled language, it is only compiled down to IR and then it's JIT compiled. In that sense JS is very similar. So I don't think interpreter vs compiler places any obstacle here. Would this be possible? That'd be a dream
Or is there a fundamental restriction that no matter how well it's designed it still needs to support all the useless parts like == operator, undefined vs null, prototypal inheritance, etc? In Kotlin's case they were able to make a language that is compatible with JVM and the toolchain, whilst not supporting 100% of weird Java parts. For example in Kotlin they have no separate primitive types unlike Java. Everything is in a consistent type system so type checking codes a lot more terse and simple
18:52 UTC
axios interceptor not triggering
why does my interceptor never trigger?
axiosConfig: https://pastebin.com/YC1Sr7Qi
loginAPI: https://pastebin.com/GxNWFjgu
authContext (React): https://pastebin.com/aNjJAHN6
i think only the first 2 are relevent, they are small but i sadly cant post them here since reddit groups up the code together and does not display well.
17:07 UTC
How to run a function?
This question is as beginner as you think it is.
I am following the mdn web docs tutorial for web development (im using Visual Studio Code) and there is a part that tells me to insert:
function multiply(num1, num2) {
let result = num1 * num2;
return result;
}
and then the tutorial just says "Try running this in the console; then test with several arguments." Just opening my website after pasting the code doesn't make anything show up? And the examples seem to imply that the answer might show up in the code itself.
Im sure this is super common knowledge but I have no clue what it wants me to do and I was never told.
UPDATE: thank you!! this has been solved! my issue was that I was stuck on not understanding the "run" action, and I totally missed the part where I didn't know what a console was yet, either. Thank you all for your help and patience
14:33 UTC
Beginner
I have just started learning js... Some tips and suggestions will be appreciated... Also I am learning by taking lectures on YouTube.. Is it correct way to learn or should I use some other source?
14:31 UTC
How to let my JS SDK know when the OAuth Authorisation flow is completed
I have a vanilla JS SDK with a django backend. I want to implement the OAuth 2 Authorization flow with PKCE for users who will use the SDK. I am using django-oauth-toolkit for the same. I have to redirect the user to the Auth page where he can give permission. Then the redirect uri points to an endpoint in my django server and the code is exchanged for access token. Everything is fine till this point. But now, how do I let my SDK know that the auth flow is complete and now I can request for the access token from the backend and start using it.
NOTE: my SDK can be used in different pages, so there is no single source of origin for any request.
12:30 UTC
Learn JavaScript Scopes In 7 Minutes
Unfortunately, human beings are not eternal creatures, and neither are javascript variables.
When a new variable is born or declared, it will be only accessible in a predefined execution context known as scope.
Check out the linked video below for a deep dive into the four JavaScript scopes.
11:42 UTC
Learning JavaScript in a week
I have a Web Development exam in a week, where I'll be asked to program a fairly simple, interactive website. I'll have to use HTML, CSS and JavaScript.
Since I had other, more difficult exams before this one, I kind of left this behind. Now I have a bit more than a week to learn everything.
Is it possible? What do you suggest I do? Should I just study my professor's old exams and try to understand and redo them, or should I watch some videos? And if so, which videos?
Any recommendations is welcome. Thank you.
09:20 UTC
Is it possible mimic Java's compareTo method in JS?
I am trying to solve a problem: https://open.kattis.com/problems/ferskastajarmid
Group 1 tests are passing, but Group 2 tests are failing even tho my solution matches this Java solution: https://github.com/moltenpanther/Kattis/blob/b72eb13f53c9b11525e037b2e11af71b06a66a96/solutions/ferskastajarmid.java#L27
I believe that the issues is with the localeCompare method, I tried to modify it and pass in the { caseFirst: 'upper' } option so that uppercase letters are sorted to be before lowercase letters, but it did not make a difference.
Any suggestions?
const n = Number(stdin());
let maxScore = 0;
let maxScoreMeme = null;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i += 1) {
const [meme, controversiality, coolness] = (() => {
const [i, j, k] = stdin().split(' ');
return [i, Number(j), Number(k)];
})();
const score = controversiality * coolness;
if (score > maxScore) {
maxScore = score;
maxScoreMeme = meme;
} else if (score === maxScore) {
if (meme.localeCompare(maxScoreMeme, 'en', { caseFirst: 'upper' }) < 0) {
maxScoreMeme = meme;
}
}
}
console.log(maxScoreMeme);00:52 UTC
QuantumMatcher library
QuantumMatcher library is a fuzzy matching algorithm that leverages bitwise operations to efficiently find approximate matches within a collection of items.
20:01 UTC
PedroReports-A LLM Powered Automated Data Analysis PDF Report Generator Tool
Hey devs! Sharing my first project - A LLM Powered PDF Report Generator! 🐍📊
GitHub: Check GitHub Repo for Video Tutorial https://github.com/bobinsingh/PedroReports-LLM-Powered-Report-Tool
This tool generates professional Data Analysis PDF Reports from any tabular dataset. You just need to input what you want to analyze, and it does the job for you. Thought you might find it interesting!
What it does:
- Takes your dataset and analysis requirements as input in the form of questions
- Uses Gemini API to generate graphs and relevant stats to answer your questions
- Generates a professional PDF with proper formatting
- Handles TOC, styling, and page numbers automatically
Tech Stack:
- Python + ReportLab for PDF generation
- React + Vite for frontend and development server
- LangChain + Gemini API for analysis
- Pandas/Numpy/Matplotlib for data processing
The workflow is simple: feed it your data, and it handles everything from visualization to creating a fully formatted report with AI-generated descriptions. No more manual report writing! 🎉
Check out the video demo! Happy to answer any questions.
18:46 UTC
Created an AI extension to handle those annoying system design questions in interviews (need frontend help to finish it)
I'm tired of getting grilled about frontend architecture and system design patterns in interviews for backend positions. After my 100th interviewer asking me to design Instagram's feed from scratch (I'm a Python backend dev, come on), I decided to create something about it.
I built a Chrome extension that listens to Google Meet captions and uses Claude API to automatically answer those typical system design questions that every interviewer seems obsessed with. You know, the ones that have nothing to do with the actual job.
GitHub: https://github.com/iklobato/interview-answers-ai
The backend is working - it captures captions, processes questions, and gets AI responses. But since I'm a Python dev who hasn't touched CSS since jQuery was cool, I need help with the frontend part. The UI is... functional, let's say. Currently looks like a Windows 98 dialog box.
What it does:
- Monitors Google Meet captions
- Detects when interviewer asks a question
- Feeds it to Claude
- Shows the answer in a floating window
What I need help with:
- Making the UI not look like it was designed by a backend dev
- Better answer display
- General frontend best practices I'm probably violating
- Chrome extension structure improvements
Before anyone asks - yes, this is partially out of spite for all those interviews where I was rejected for not knowing the intricacies of frontend caching strategies when applying for a Python API position.
If you're interested in contributing, check out the repo. And yes, I know using AI in interviews is controversial, but so is asking a backend dev to design a responsive mobile UI in 2025.
Edit: This is obviously meant for practice/mock interviews, not real ones.
15:28 UTC
Hp constantly decreasing in JS game *help*
Hey! This might not be related to this sub but i need help with my JS game.
- It's a clicker game where you have to destroy blocks by clicking them and when they pass out of the screen you lose hp.
- For some reason due to a bug the hp is decreasing when the boxes dont even pass the screen idk what's causing that i checked out everything, have no unknown refrences but still it decreases due to some flaw.
To those interested in taking a look:
Here's the code at github: yaseenrehan123/Falling-Blocks: A game about destroying falling blocks
Demo at Codepen: Hp drops unintentionally!
Here is also the game at website so you can try it firsthand: Falling Blocks
Any sort of help would be appreciated!
15:02 UTC
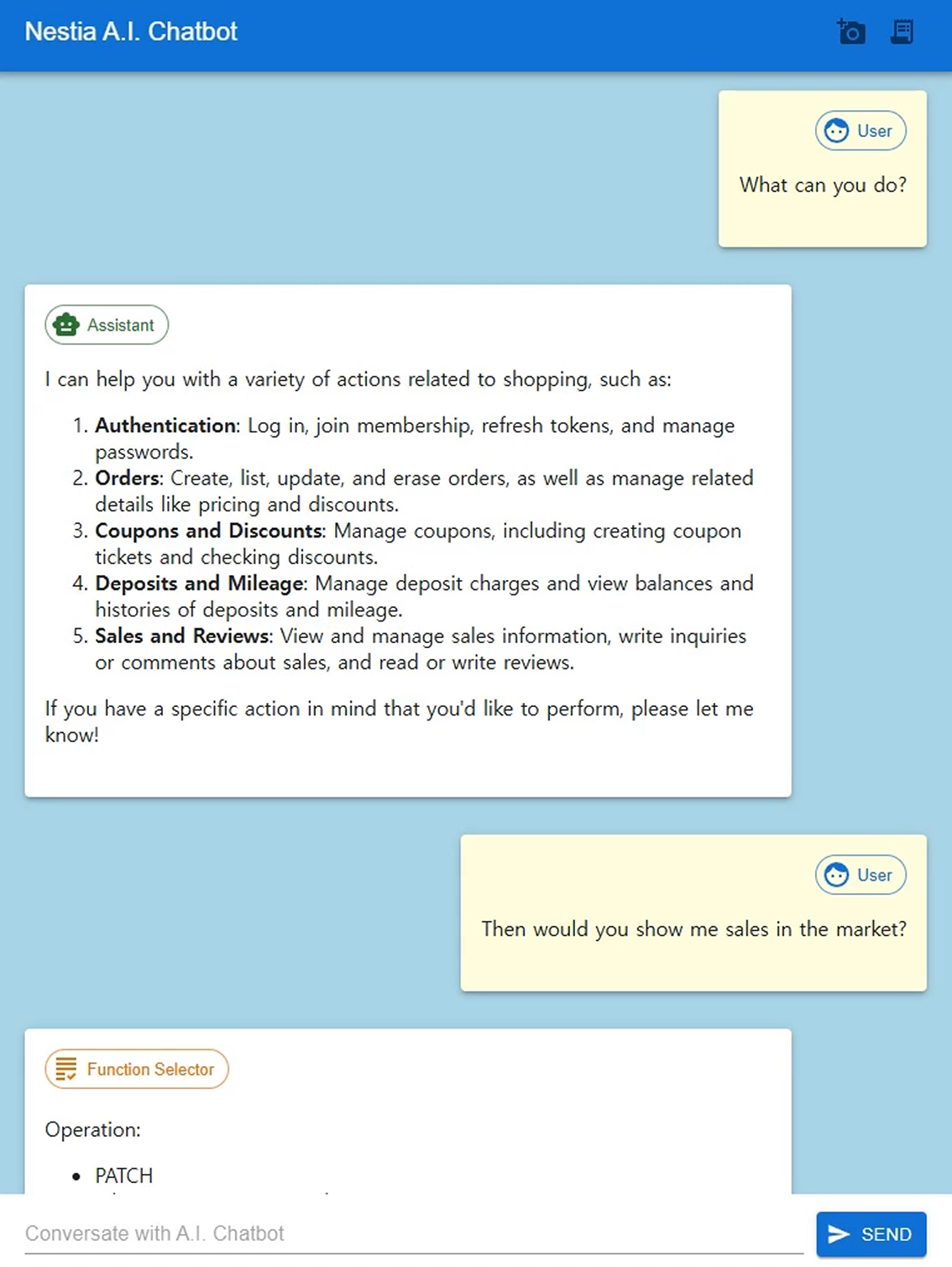
I made Swagger Chatbot (evevry backend servers also can do it)
I've succeeded to make the shopping mall agent just by converting shopping mall backend server's Swagger document to the OpenAI's function calling schemas. Even though response time of the agent is a little bit slow, I could see the future's application. A.I. chatbot is the future.
Anyway, I've published all of the conversion processes as open sources to share this concept with you. Let's go to the new A.I. era's application development with me. Just develop backend server with well-documented Swagger, and just convert it to the function calling schema. That's all.
Even though the A.I. chatbot can't conquer every frontend developments, it can replace many things, and more efficient and user-friendly than the traditional GUI applications. This concept is called Super A.I. chatbot, and I believe that it will change the application development ecosystem a lot.
- Detailed Article Link: https://nestia.io/articles/llm-function-calling/ai-chat-with-your-backend-server-every-backend-servers-can-be-super-ai-chatbot.html
- Guide Document: https://nestia.io/docs/swagger/chat
- Demonstration Videos
- Shopping Mall (E-Commerce): https://youtu.be/m47p4iJ90Ms
- BBS (Bullet-in Board System): https://youtu.be/pdsplQyok8k
- Related Repositories
@nestia/chat: https://github.com/samchon/nestia@samchon/openapi: https://github.com/samchon/openapi
In the next time, I'll show you the seller's agent application which can create and manage the products just by few conversation texts. As you know, the seller's application is very huge and even just product creation part is composed with dozens of pages due to the complicate SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) structure. And its post management is much complicate. However, these complicate applications can be replaced just by a A.I. chatbot composed from the Swagger document.
And in the next month, I'll demonstrate you much more amazing concept, that is building such function calling A.I. chatbot which can ben developed by even someone who does not know the programming at all.
13:32 UTC
Tech Stack for LLM-Based Web App?
Is it wise to be fully dependent on Vercel AI SDK now given they are still a bit early?
Also heard that developing with next.js + vercel AI SDK is such a breeze using v0 guided coding.
But it is really a quickly adapting and production reliable tech stack? Or is it just easy for beginners?
12:23 UTC
My code doesn`t work in browser
https://pastecode.io/s/qzdr2dhk
It asks for input yet returns nothing. chatgpt has no answer neither deepseek
09:12 UTC
How do i ask my question?
Reddit is messing up my code. I can`t upload images. What should i do
08:57 UTC
Flatten an uneven data set
How can I turn this:
data = [ {"parents": ["1235"],"size": "100","id": "abc100","name": "Test1"}, {"size": "200","id": "def200","name": "Test2"}, {"parents": ["abcdefg"],"size": "300","id": "Test3"} ]into this:
mod_data = [ {"parents": "1235","size": "100","id": "abc100","name": "Test1"}, {"size": "200","id": "def200","name": "Test2"}, {"parents": "abcdefg,"size": "300","id": "Test3"} ]. I've tried output = [].concat.apply([],data); and output =data.flat(); but the parents element remains a [].
20:42 UTC
Im looking for the complete javascript course of Jonas Schmedtmann
Hi guys, do you know where i can download the 2025 version? thanks
17:54 UTC
What are the best platforms for learning JS and TS?
Please share the best places to start learning JS—maybe some useful books or websites. I'm interested in everything!
17:30 UTC
I'm a beginner and I can't create any Projects!
Hello this is someone who recently got into coding and has grasped the basics of HTML, CSS and JS and I would like to ask all the experienced web devs out there about this one issue I am always encountering. I can't make any actual projects without seeking for a tutorial and often times my code is messy it's unorganized and I can't really do much of anything without watching tutorials. I always make sure to try to do something on my own before leaning on a tutorial but 90% of the time what I create either doesn't work or just is too messy for even me to understand and when i look at the tutorial i find the teacher to use functions and all the other methods in a way I never could've imagined using myself. I mean what i attempt to make in like a 100 lines of code is done by them in like 50 lines or less and it would be really helpful if someone who's well experienced in this field would guide me through these times where I feel like I'm not improving at all and I just feel like I'm basically copy pasting the code that I see on my screen. It would mean alot to me if someone guides me...
17:27 UTC
Measuring Distance Between Objects: Lessons From a Tower Defence Game
I recently wrote an article in which I measured the distance between two objects using JavaScript.
This helped me determine whether an enemy is within a tower's range.
Check it out and drop your thoughts in the comments!
16:15 UTC
How to Implement Cursor Keys to navigate a complex layout?
Hi Folks, i'm making a card game in Javascript.
Cards can move to multiple different hands and decks, and at any point in time the range of things that can have focus can change quite quickly.
I have it so the DOM changes properly and the cards (<figure/>) are properly reparented into their decks or hands (<section/>). They are given a Tab Order explicitly and this works fine and logically, for any given moment. BUT!
Since layout matters, I'd also like to be able to implement cursors as WASD to move around the cards and decks.
I could envisage making a list of links in the data to say what is up, down, left and right of each other, but as both the positions of things, and whether or not they're focusable, can change quite a LOT and I don't like the idea of re-creating a data structure for this every time the game state changes.
After all: it's all there on the screen.
So is there an obvious way to figure out which focusable object is the closest to the current one, in given screen direction.
I'm struggling to come up with the best way to think about this problem - what other approaches would make sense?
Thanks!
15:46 UTC
Resources or Advice about Project? (New To Coding)
I'm rather new to coding, but I've grown interested in it recently, especially due to a personal project I'd like to undergo. One major roadblock I'm hitting at the moment is that I'd like to pull from a table in a database or such (like I've currently got information in a google sheets doc) and have it auto populate based on the name entered in the main spot.
Basically, if I put a name into a text box, it should auto populate the appropriate information correlating with said name from the data table.
I know typing out a full answer might be difficult and I'd honestly like to understand the why, not just the how. So if anyone knows of some resources that might be able to help, I'd be so very grateful!
07:16 UTC
Tutorials with low-level code
Built a calendar library with js, I am wondering if there are tutorials on how to build 2d canvas library, 2d animation library, 3d rendering engine or similar.
03:28 UTC
Need help with document.getElementsByClassName() and an extra variable....
Say that I have these html strings....
<input class="SUBMIT_BUTTON" id="SUBMIT_BUTTON_1" refID='clock' type="submit" value="Clock">
<input class="SUBMIT_BUTTON" id="SUBMIT_BUTTON_2" refID='radio' type="submit" value="Radio">
I don't want to get hung up on the names..... just assume I have to work with these.
I know that I can do something like this in javascript:const buttons = document.getElementsByClassName("SUBMIT_BUTTON");
but how can I pick the refID='clock' or the refID='radio' elements?
I need to be able to drill down to:
class="SUBMIT_BUTTON" refID='clock'
or the
class="SUBMIT_BUTTON" refID='radio'
elements so I can change the text of the button on either of those elements.
I know how to reference them by ID or by CLASS, but not by CLASS[refID='clock'] or CLASS[refID='radio' ]
- thanks
02:56 UTC
Need help with document.getElementsByClassName() and an extra variable....
Say that I have these html strings....
<input class="SUBMIT_BUTTON" id="SUBMIT_BUTTON_1" refID='clock' type="submit" value="Clock">
<input class="SUBMIT_BUTTON" id="SUBMIT_BUTTON_2" refID='radio' type="submit" value="Radio">
I don't want to get hung up on the names..... just assume I have to work with these.
I know that I can do something like this in javascript:const buttons = document.getElementsByClassName("SUBMIT_BUTTON");
but how can I pick the refID='clock' or the refID='radio' elements?
I need to be able to drill down to:
class="SUBMIT_BUTTON" refID='clock'
or the
class="SUBMIT_BUTTON" refID='radio'
elements so I can change the text of the button on either of those elements.
I know how to reference them by ID or by CLASS, but not by CLASS[refID='clock'] or CLASS[refID='radio' ]
- thanks
02:56 UTC